5 Cybersecurity Trends Every CISO Needs to Watch Out in 2023

We are again at the time of the year when we put on our astrologist hats to predict the future and prepare for the new cybersecurity trends. With the year-end just a month away, we need to map out new projects, estimate budget requirements, plan against new attacks, and look out for the latest guidelines and regulations in the realm of cyber security.
In recent years we have witnessed a continuous transformation in the digital world. The impact of the hybrid work model, significant IT infrastructure changes, and how businesses operate, and handle data have made the cyber security landscape more complex and dynamic.
Based on last year’s statistics, cybercrime is up by 600% from the covid-19 pandemic. In 2021, the average number of cyberattacks and data breaches increased by 15.1% from previous year. All this data estimates the global annual cost of cybercrime to be $6 trillion in 2021 – this would be the third largest economy in the world if cyber security is a country!
This analysis clearly shows us cyber security’s increasing scale and scope in 2023. Also, the high probability of global recession that is anticipated next year makes the situation more challenging.
Here are some cyber security trends that will dominate the cyber landscape in 2023 and beyond.
Top 5 Cybersecurity Trends 2023
The Evolving Role of a CISO
With the advent of digitization, data security has become very mainstream. Also, cyber security regulations such as GDPR, PCI DSS and SWIFT CSF have become mandatory for businesses. We have seen numerous digital attacks worldwide on IT, IoT and OT devices. It has become imperative that companies and even individuals make security decisions to reduce the attack surface and protect themselves from data breaches.
This change in perception and levelled-up priority for cyber security across executives and leaders increased the role and responsibility of CISOs. The introduction of 5G technology, evolved AI software & applications, increased IoT devices, the trend of hybrid work models, and stringent mandatory regulations increased the challenges for CISOs.
The work of CISOs will hence become more complicated and involved. They need to keep track of all the advanced attacks and regulations. Also, CISOs need to learn and use the latest technologies to defend against upcoming threats in the modern world.
Increasing Attacks on the Healthcare and Automotive Industries
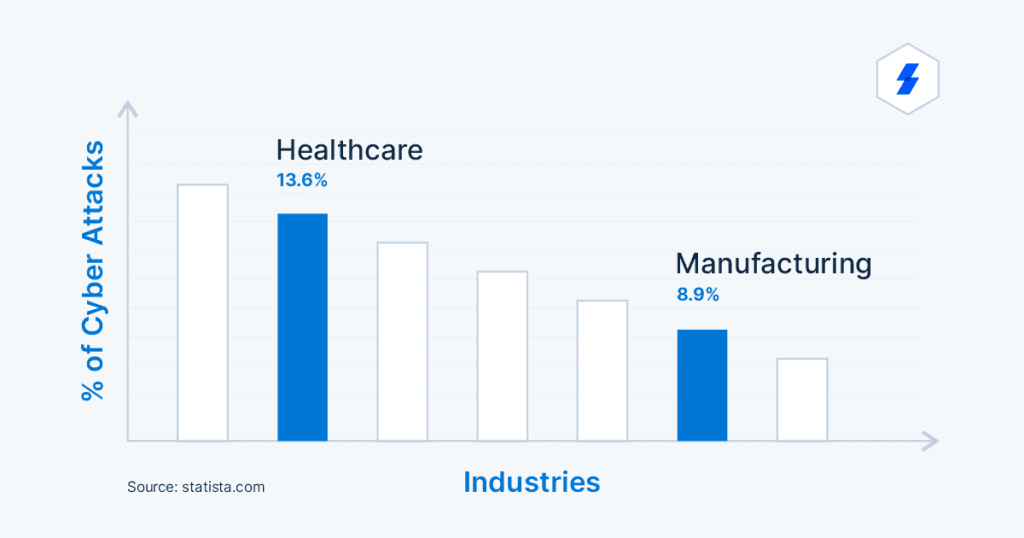
Virtually all industries experience cyberattacks, but some are serious. In 2021, as per Statista, Healthcare (13.6%) is the 2nd largest attacked industry, Manufacturing (8.9%) being the 6th largest, attacks on automotive industry are expected to rise to peak as IOT technology dominates the industry going forward. Looking into the future, due to technological advancements, it is predicted that the automotive and healthcare industries will be the top priority for attackers to exploit.
There is a good correlation between these two industries regarding the technological developments they are undergoing. Healthcare awareness is up by a minimum of 3 times after the recent global pandemic. The availability of profound technology support boosted the need for awareness. We have never seen any industry rise digitally so quickly as healthcare after the covid-19 pandemic. AI drives the results of many scans and tests in this modern healthcare era, so attackers will be keen to exploit this new trend.
Individuals’ health information will be a huge target, and CISOs must protect individuals and the industry from such new focused threats.
Rising Risk Exposure with Proliferating IoT Devices
IoT (Internet of Things) made device communication a common phenomenon from what was not less than a miracle a decade ago. Nowadays, every device, either a personal or a business device, is connected to at least one other device for seamless customer experience and ease of data handling. All the smart devices currently in trend are intensely powered by IoT. For example, smartwatches are the new trend and are connected to several other appliances. Smart TV, automatic cars, and smart display panels are operated with connected technology.
This IoT world can increase the risk exposure multi-fold for each enhanced connection. The growth of 5G can make it even more complex. Supply chain attacks and DDOS attacks are increasing widely with new and advanced versions of them every day. These threats exploit the interconnection very well and prove IoT to be making the customer’s experience seamless and the hackers. This shows how CISOs should be careful while designing security frameworks across domains.
The Need for Cloud Security
Security measures must be continuously upgraded and monitored to safeguard the data from leaks in the cloud. As numerous organizations are migrating to the cloud, the scale of cloud services will increase at great pace in 2023.
Remote work poses new cyber security risks, especially for cloud applications. This risk multiplies due to a lot of unsecured connections. Many employees use personal devices and even mobile applications for instant messaging. Even two-factor authentication is mostly redirected to their personal devices. As most of these applications are cloud-hosted, even one vulnerability exploited is prone to make the entire organization vulnerable.
So, CISOs need to focus on securing cloud applications with a double layer of protection and ensure the best in 2023.
Surge in Ransomware & Social Engineering Attacks
Ransomware has become the new business model for hackers. The return on investment in ransomware is the highest. So, attackers are coupling every threat with ransomware as an add-on to double their profits. This trend is projected to become deadly for organizations in 2023.

Also, the fact that every human is prone to make errors is used to exploit enterprise users with social engineering attacks. This technique has become a primary mode for bypassing network security. Hence, this avenue for attack targeting individuals using human psychology at the core of the attack design has proven to be very productive for hackers.
Related Reading: Secure what matters in 2023! Read our Privileged Access Management guide to understand access security’s relevance in the coming years.