High Availability to Eliminate Single Point of Failure

High Availability to Eliminate Single Point of Failure
The advancement of the IT landscape has witnessed an evolution of business demands and requirements. Organizations are devising strategies to avoid critical failover and ensure business continuity – aspects like Performance, Downtime, Traffic Volume Management, No Interruptions and Service management are considered in addressing this goal.
Adopting a set of best practices that help achieve high availability for your service is the most effective strategy to avoid downtime and reduce losses.
What is High Availability (HA)?
High availability (HA) is a feature of a technological system that eliminates single points of failure to provide uninterrupted operations or uptime. High availability clusters are collections of servers that handle mission-critical applications with low downtime and constant availability.
Nowadays, systems across an organization’s IT infrastructure anticipate HA to restore normal operations in a matter of minutes or less, with little or no data loss.
How Does High Availability Work?
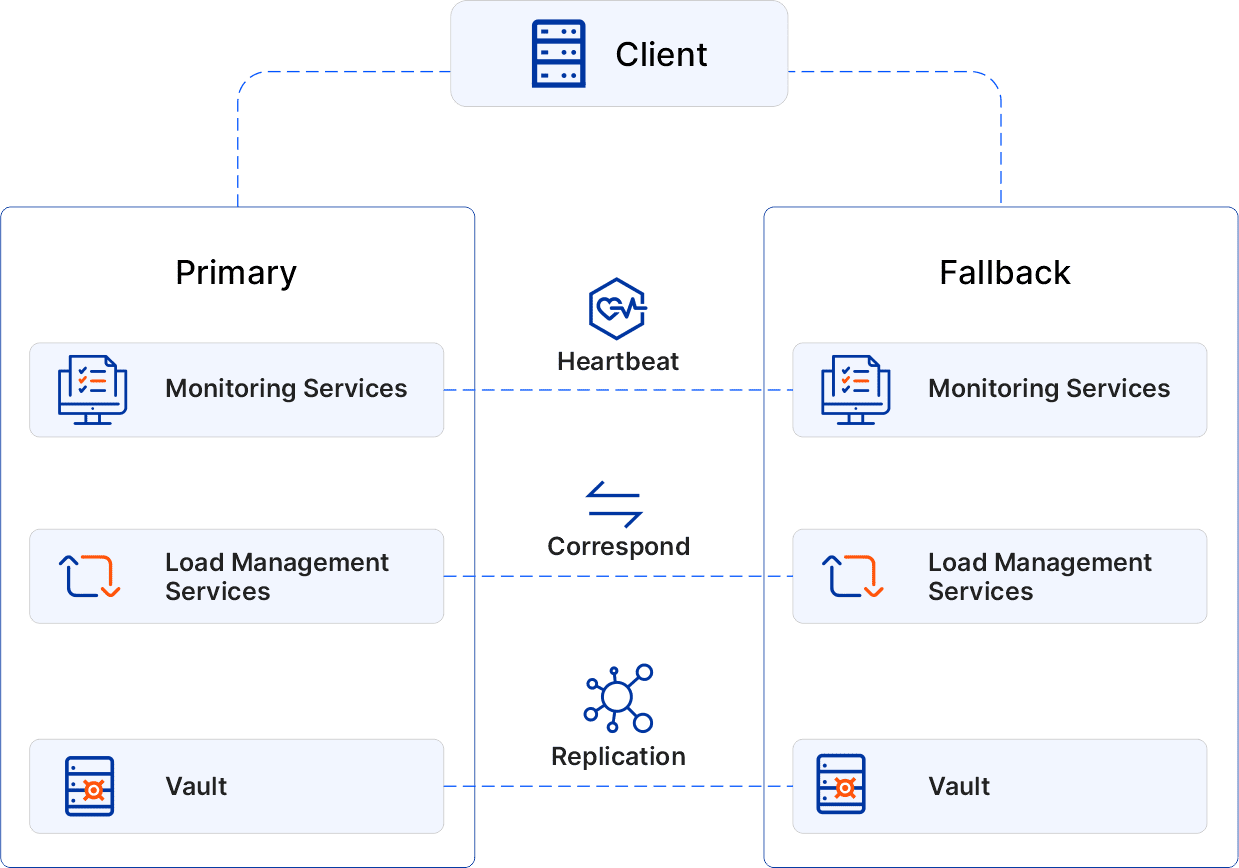
Sectona PAM provides a variety of High Availability scenarios and options to help develop HA strategies for solutions. The HA functionality ensures that the application and vault are always available.
Sectona has various vault options, and the technique for managing HA differs depending on the vault. The system’s availability is determined by multiple factors, including the number of components, configuration settings, and the resources assigned to each component.
The number of failover combinations in a system with HA strives for a 99 per cent uptime with near-zero downtime. Clustering and load balancing are essential components for a high availability Sectona Web Access setup. The system comes with a built-in software-based load balancer and support for an external load balancer.
A load balancer distributes incoming user requests throughout a cluster to reduce response time and avoid overwhelming any single node. The load balancer also sends the user the response from the chosen server and performs three critical tasks. It distributes traffic among several nodes cost-effectively, ensures HA by only forwarding traffic to active nodes (by health check monitoring), and gives the ability to add and remove nodes.
Sectona uses load balancing to provide good availability when a system has many users. Load balancing automatically assigns workloads to system resources, such as sending various access requests to different jump servers. The load balancer determines which system resource best suits each workload. Using numerous load balancers to accomplish this assures that no single jump server is overburdened.
Use Cases:
- Managing failover
The primary goal of High Availability is to remove Single Points of Failure (SPOF). Sectona achieves this by implementing a system that uses redundant servers to execute several instances of services simultaneously. In the event of a primary server failure, the fallback server takes over. If one server fails, the system can fail over to another server that is not affected. Server A, for example, is our primary server, while server B serves as a backup. If server A goes down, the system will route the user’s traffic to server B.
Sectona provides 1+1 instances to ensure that Sectona Web Access and vault components failover in the event of a failure.
- Sharing the System Load
Sectona includes built-in application load balancing to configure two web access nodes in Active-Active mode with a defined priority. The client request will always be handled by the priority-1 (P1) node, which will check the number of sessions operating on each node and resource consumption to determine which node will handle the request.
The node with the fewest concurrent sessions and resource utilization will always serve the request compared to other nodes. In a node loss, the online node will fulfil all incoming requests as the P1 node. Sectona enables failover with a 1+1 node.
Sectona also assists with external load balancing, which can be configured using a hardware or software load balancer with a specific operating system. It distributes web application traffic over a cluster of application servers.
It is critical to configure session persistence when using Sectona Web Access with an external load balancer. Session persistence is a procedure in which a load balancer creates an affinity between a client and a specific network server for the duration of a session. Sectona’s External load balancer supports 1+n nodes for failover.
Benefits:
- Minimum Downtime
HA solutions allow you to move operations smoothly to a host server if one of your servers fails. If one business-critical server goes down, it will bring down all other servers that interface with it. Client relationships will be preserved, staff will be able to complete their tasks, and vital corporate functions will not be jeopardized by downtime.
- Easy Maintenance
Unplanned disaster downtime isn’t the only sort of downtime that businesses suffer. Companies may also be subjected to costly downtime due to hardware and software updates or upgrades. This downtime can be reduced with an efficient HA solution.
- Maximum Flexibility
Businesses can prepare to restore their server to the host location and continue to operate production while their internal operations are adjusted. HA solutions enable flexibility in cases where the production site must be operational and secure 24×7. Individual server partial failover permits communication between various interfaces. When the main production site is back up and running, the failover site may be easily turned off, and any modifications made while the main site is down can be transferred back to production servers.
Related Reading: How to Deploy a Multi-Site PAM?