Here is Your Enterprise Cyber Hygiene Checklist for 2023
2022 has shaped up to be a pricey year for victims of cybercrime. Cyber attacks plagued the world — interrupting businesses and often leading to damaged corporate reputations and massive ransomware payouts. This, in turn, has given rise to a buzzword pertaining to operational resilience - cyber hygiene.
Before we delve deep into the concept, let us first look at some of the costliest data breaches of recent times.
Some of the Costliest Cyber Attacks in Recent Times
The cost of a data breach heavily depends on the number of compromised records. According to the Ponemon Institute’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2022, breaches that affect from 1 – 10 million records cost $52 million on average.
Having said that, in the last few years alone, we have witnessed cases that cost even more than that:
This is a textbook example of an organisation that suffered for years from a single data breach. By mid-2021, British Airways faced an £800 million (≈ $1 billion) class action lawsuit from cyber attack victims.
Context: In 2018, hackers stole the personal records of over 420,000 British Airways customers and employees. In 2020, after a thorough investigation, the company was fined £20 million (≈ $27 million) for its inadequate data protection system. Adding to the misery were the compensation claims in 2021 – with an estimated 2,000 per victim, amounting to 800 million liabilities.
A cyber attack on Medibank, a health insurer, affected all its 9.7 million current and former customers. Criminals demanded a ransom payment of $10 million, which was later reduced to $9.7 million ($1 per affected customer), not to publish the stolen information, which Medibank refused to pay.
The threat actors then threatened to release some data each day the ransom remained unpaid. Even before regulatory and legal costs, and customer compensation, the attack was estimated to cost Medibank $25 – $35 million.
The Equifax breach of 2017 remains one of the catastrophic cyber attacks. The Personally Identifiable Information (PII) of around 143 million people was stolen from the credit reporting agency. The initial intrusion reportedly occurred through a software vulnerability.
After the incident, Equifax spent a whopping $1.4 billion to upgrade its security posture.
The demand for cyber security is now more than ever. To reduce the financial and reputational damages that data breaches cause, the concept of cyber hygiene has gained prominence.
What is Cyber Hygiene?
Cyber hygiene refers to the practices and measures that individuals and organisations take to protect themselves from online threats and ensure the safety and security of their digital assets. It involves adopting good cyber habits and behaviours that reduce the risk of cyber attacks.
An example of good cyber hygiene is keeping software and applications up to date. Hackers often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain access to systems and steal data. Regularly updating software and patches can help prevent these types of attacks.
Why is Cyber Hygiene Important?
Cyber hygiene enhances your systems’ overall well-being and protects your sensitive data. It is essential to an organisation for several reasons.
- Risk of Cyber Attacks: Poor cyber hygiene practices can expose systems to cyber attacks, such as viruses, phishing frauds, spyware, and malicious code injection.
- Data Breaches: Weak passwords and outdated software may lead to security breaches, providing cyber attackers access to sensitive and confidential information and impacting data privacy and integrity.
- Financial Losses: Poor cyber hygiene habits may result in financial losses for the organisation, including fines, penalties, and remediation costs.
- Legal and Regulatory Consequences: Failure to comply with strong cyber hygiene measures can lead organisations to face severe legal liabilities.
- Reputational Damage: Data leak scandals and other cyber attacks can damage a company’s reputation and discourage customers from trusting it again.
The goal of cyber hygiene is to create an intelligent and structured environment that minimises the risks of external contamination without having to spend lots of IT effort frequently.
This way, you and your team have more time to use the environment more productively and strategically, thereby generating good business results.
Here is Your Cyber Hygiene Checklist
Now that we have established the ‘why,’ we must address the ‘how’ – How does one go about maintaining good ‘Cyber Hygiene?’
We’ll look at some standard practices first.
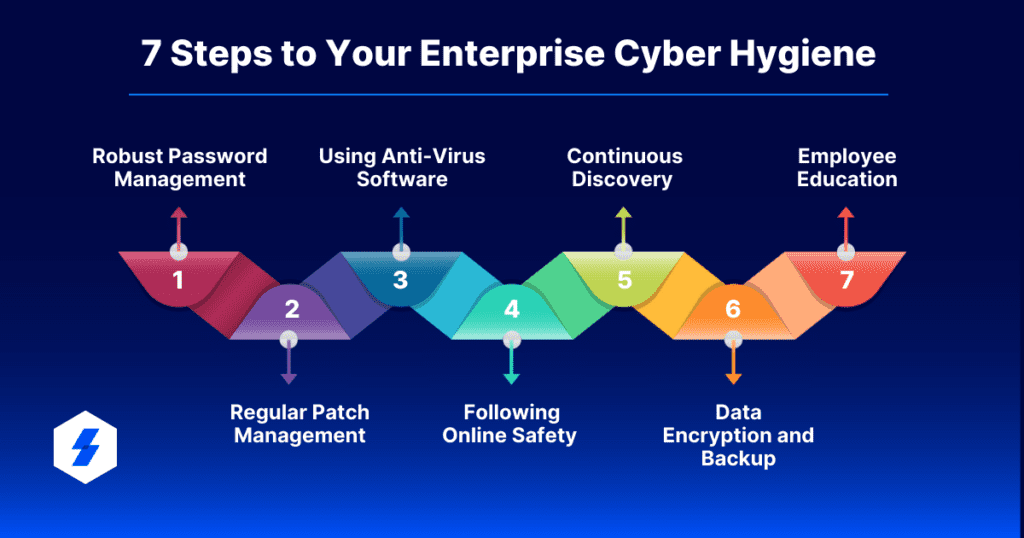
Standard Practices of Cyber Hygiene
Password Hygiene - best practices and habits that individuals should follow to protect their online accounts from unauthorised access. Here are some tips for good password hygiene:
- Use a Unique and Strong Password for Each Account: Do not use the same password for multiple accounts; it makes it easier for attackers to access all your accounts if they can obtain one password.
- Use a Long Password: The longer the password, the harder it is for attackers to guess. Try a mix of numbers, upper and lowercase letters, and symbols to make the password more complex.
- Avoid Frequently Used Words and Phrases: Avoid using easily guessable information like your name, birth date, or the word “password” as your password.
- Change Your Passwords Regularly: It is a good idea to change your passwords every few months to reduce the risk of an attacker accessing your account.
Patch Management
The process of identifying, acquiring, testing, and installing patches (software updates) on computer systems or other devices to address and fix known vulnerabilities, bugs, or other issues.
Anti-virus Software
Install anti-virus software and keep it up to date. This software helps detect and remove viruses and other malicious programmes.
Being Safe Online
- Be Cautious of Public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi networks can be insecure and allow hackers to intercept data. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive activities, such as online banking or shopping.
- Be Cautious of Phishing Emails: Be cautious of emails that appear to be from a trusted source but are designed to trick you into revealing sensitive information. Do not click on any links they contain.
- Use Email Filtering to automatically identify and block unwanted or unsolicited emails, such as phishing emails, scams, or promotional emails.
Data Encryption and Backup
In practice, it is important to both encrypt and back up your data. Encryption helps keep your data secure, while backups ensure that you can still access your data even if the original copy is lost or damaged. It is also important to store backups securely, ideally in a different location from the original data, to prevent data loss due to disasters such as fire, flood, or theft.
Asset Discovery
The process of identifying all the devices and resources that are connected to a network, including computers, servers, routers, switches, printers, and other network devices. The goal of asset discovery is to create an accurate and up-to-date inventory of all the assets in a network. Once the assets in a network have been identified, they can be classified and prioritised based on their criticality, vulnerability, and importance to business operations.
Employee Training
Train employees on security best practices to help them understand how to identify and avoid potential security threats.
That being covered, if you want to take your organisation’s cyber security measures up a notch, you might want to implement the following Special Practices of Cyber Hygiene.
If you have a spread-out workforce involving remote devices and cloud storage, it is imperative that you implement specific practices to secure them as well.
- Implement Access Controls: Establish strong access controls to restrict access to your cloud resources. Use multi-factor authentication, access policies, and encryption to safeguard your data.
- Monitor Your Cloud Resources: Continuously monitor your cloud infrastructure for any unusual activity, such as unauthorised access or configuration changes.
- Use Encryption: As with the data on your system, encrypt the sensitive data stored, transmitted, and processed in the cloud as well to ensure that only authorised parties can access it.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Segment your cloud network to minimise the impact of a potential security breach.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan: It ensures that you can respond effectively in the event of a security breach.
By following these best practices, you can significantly improve the security of your cloud infrastructure.
How Will Sectona PAM Address Your Company’s Cyber Hygiene Needs?
Sectona Privileged Access Management (PAM) is designed to manage and secure privileged accounts and access to critical systems and data within an organisation. As it pertains to cyber hygiene, here is what Sectona PAM offers:
Privileged Account Discovery and Security: Sectona PAM helps stay in control of newly added IT assets and unknown or hidden privileged accounts spread across your IT. Now, you can leverage comprehensive yet flexible asset discovery techniques using network scans, AWS resource discovery, Azure discovery, VM (virtual machines) ware and Hyper-V resource scan, and Active Directory scan.
Password Management: Manage and rotate not just passwords but SSH keys as well with embedded and encrypted vaulting.
Remote Device Security: With Sectona PAM, you can provide outsourced team users secure access to organisation resources. You can enable need-based, VPN-less remote access for the modern workforce. Moreover, you can maintain complete session isolation between remote machines and critical servers across hybrid environments, securing them with Sectona PAM.
Privileged Account Analytics: Advanced session monitoring for all privileged activities with risk-profiling and behaviour-based analytics.
Privileged Account Creation, Management, and Deletion: Irrespective of the privileged accounts you use (named, service accounts or shared accounts), create, manage, and delete them with built-in rules and workflows, with complete auditability.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Neutralise the risks associated with compromised credentials by enforcing multi-factor authentication for all access layers.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Access: Grant users’ access to specific resources, data, or systems only when they need it to perform their job duties or tasks. Define custom JIT access methods (Enable/Disable, Provisioning/De-provisioning) for securing assets based on user access type.
Endpoint Privilege Management: Control and limit the access privileges of users and applications on endpoints such as desktops, laptops, servers, and mobile devices.
Cyber security Compliance: Help your company comply with several laws, regulations, and standards, such as GDPR, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and PCI, among others.
Improve Your Cyber Hygiene Today
Ready to get started? Contact us for a detailed conversation pertaining to everything mentioned above… and more.